Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy (fibro-colonoscopy (FCS), video-colonoscopy) is a «gold» standard of colon and rectal examination.
This procedure carried out by doctor, and permits to evaluate the intestinal surface by spatial probe. This method is the most informative and specific for polyp, cancer and inflammatory bowel disease (Ulcerative colitis, Crohn`s disease ecc.) detection. This procedure permits to investigate colon totally in 90% of cases.
Colonoscopy should be applied every year to patients after 40 years old. During video-colonoscopy patient also can observe by monitor procedure, and after examination to get the record of procedure. Colonoscopy can by diagnostic (visual evaluation of intestinal surface, chromoendoscopy, endoscopic ultrasound, biopsy, and punition) and operative (plypectomy, tumorectomy, mucosectomy, healing of bleeding, extraction of foreign bodies, colon stenting ecc.).
Equipment
Colonoscope is special device, which is represented by thin, flexible, guided probe (1,4 to 2,0 miters). There are two types of colonoscopies: fibro-colonoscopy and video-colonoscopy. During fibro-colonoscopy, images are transmitted by optic fiber, that’s why colors are not always identical with real. Disadvantages of fibro-colonoscopy also include absence of magnification function, of ultrasound scanning, presence of only one canal. Optical fiber can be easy damaged. That’s why video-colonoscopy becomes very popular. That is new generation of endoscopic equipment is fitted up by micro-video camera instead of optic fiber. The quality of imagine is much better and it can be recorded by video or DVD. These endoscopes can have two canals, ultrasound scanner and permit 160 – multiple magnifications. Ultrasound scanner is important to evaluate tumors.
Indications
1. Presents of suspicious symptoms
- Rectal bleeding
- Presents of mucus in feces
- Constipations or diarrhea
- Stomachache
- Inexplicable fiver, weakness and fatigue
2. Suspicious results of laboratory and instrumental examinations
- Records of CT, X-ray, ultrasound examinations and capsule endoscopy
- Inexplicable blood disorders (deficit of hemoglobin, erythrocytes cc.)
- Increased level of cancer markers (CEA, CA 19-9)
- Positive fecal occult blood test (FOBT)
3. To exclude colon cancer in case if patient has
- Polyps of stomach
- Polyps of rectum
- Before gynecological operation (endometriosis, ovary and uterus tumors ecc.)
4. Patients with higher-than-average risk of colon and rectal cancer (they should be checked every year)
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohn`s disease
- Operated colon in the past (because of oncology disease)
- Colon polyps in the past
- Family history of polyps or colorectal cancer
Technique of colonoscopy in our clinic
Mostly colonoscopy is e well-accepted method. Comfort and decreasing of pain during procedure are provided by several factors. First of all, patient should be preliminary informed about technique of procedure and about possible discomfort. In this case, patients are emotionally prepared and easy follow to instructions of doctor and nurse, this behavior minimizes discomfort. Anesthetics provide relaxation of intestinal muscles. We also use only the most modern equipment. Therefore, if experienced doctor with modern equipment carries out colonoscopy in good clinic narcosis is not required. Keeping to disinfection standards excludes the risk of infection.
In proctology department of Kiev regional hospital colonoscopy is carried out in colonoscopic cabinet, which is appointed by bi-canal (operative) video-colonoscope Olimpus Evis Exera T160L. Patients are provided by disposable close. Colonoscope is moved in rectum through anus and carried out up to cecum (or ileum). Air insufflations permit to extent colon. After procedure air is aspirated and patient doesn’t feel discomfort. Patients with adhesion process in abdomen can feel some pain during procedure, which is minimized by medications. When doctor achieves cecum examination is not finished yet. Removing endoscope he continue look over colon surface. Procedures are recorded by DVD. Bi-canal video-colonoscope permits us provide not only diagnostic screening colonoscopy but also specialized diagnostic and operative procedures.
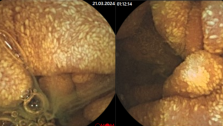
1. Chromo-colonoscopy .
Contrast stains, such as methylene blue or indigo carmine are used to increase the contrast between lesion surface and nearby tissue and this way identify borders of dysplasia. This procedure permits to identify malignant and pre-malignant disorders, real dimensions of tumor and choose right position for biopsy.
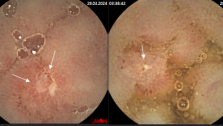
2. Biopsy of all suspicious sites should by carried out. Biopsy can be provided by loop, forceps. This manipulation is painless and quick.
3. Ultrasound examination
This scheme shows intestinal layers, zone of reflection (inferior one) and example of cancer invasion in intestinal wall (superior one).
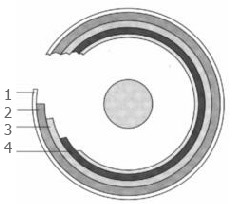
1. Muscular layer. 2. Submucosa. 3. Mucosa 4. Zone of reflection.
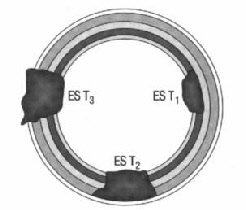
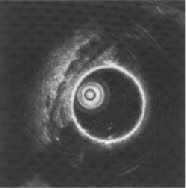
Left part of photo is a scheme of normal intestinal wall. This method is used to identify depth of inflammation or invasion (for tumors) and malignant changes in adenomas.
4. Diagnostic or operative punctures of formations of mucosa and submucosa.
5. Polypectomy.
6. Mucosectomy is excision of involved mucosal sector (sectors with dysplasia, sessile polyps, villous adenomas) after chromo-colonoscopy.
7. Tumorectomy is excision of early colon tumors by several endoscopic instruments. Stadium of cancer (depth of invasion) should be identified before operation by endoscopic ultrasound examination.
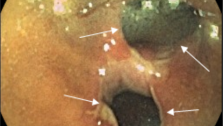
8. Endoscopic stenting is method of colon practicability reconstruction by stent. Indications for this technique are palliative treatment or preoperative preparation patients with cancer obstruction.
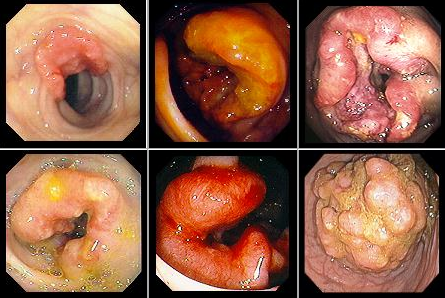
Differential diagnostic and verification of colon diseases by colonoscopy
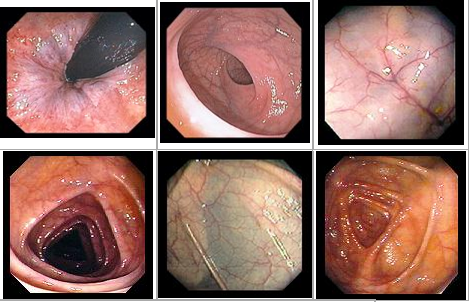
Normal endoscopic colon imagine
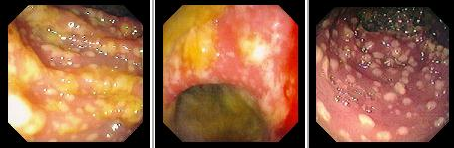
Antibiotic-associated colitis
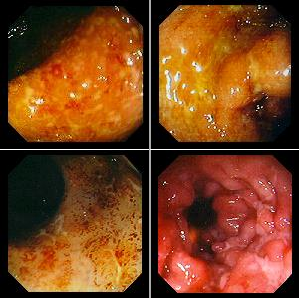
Ulcerative colitis
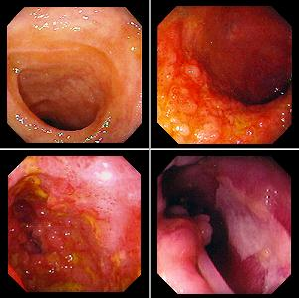
Crohn`s disease
Villous adenomas
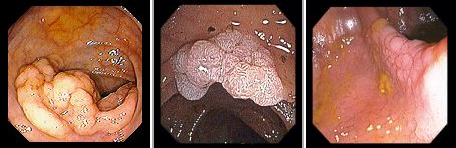
Polyps
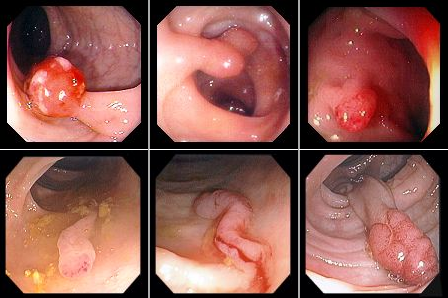
Colon cancer