Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are the most common diseases of the rectum.
Word «hemorrhoid» translated from Greek language means «bleeding», which directly connected with the most prevalent symptom of this disease – there is blood outflow from anus. Every year amount of patients, who suffer fro this disease, increases. By the way, mostly there are able to work-age patients. The incidence of hemorrhoids is quite high (118-120 cases among 1000 adult people) there is from 34% to 41% of all patients who have colon or rectal pathology. The prevalence of hemorrhoids is the same in both sexes. Acute hemorrhoid thrombosis often occurs among pregnant women, mostly during third trimester.
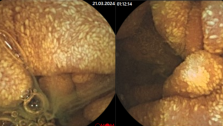
Hemorrhoids are characterized by dilatation of cavernous bodies, which are located in 3-5 points above the dentate line and degenerative changes in suspensor ligament (Park’s ligament) that maintains the vascular structures.
There are predisposing factor, which can be reason of hemorrhoids:
- Constipations increase the pressure in rectum and arterial blood flow in cavernous bodies amplifies. That becomes the reason of dilatation and prolapse of cavernous tissue.
- Heritable factors. Often hemorrhoids become family disease.
- Pregnancy and childbirth. In these conditions pressure in woman`s abdominal cavity increases that can be reason of hemorrhoids.
- If patients has a habit to sit a lot his muscles are relaxed for a while, which is the reason of suspensor structures weakness.
- Low-mobile life style is the reason of blood stasis in pelvis which determines of dilatation of corpus cavernosum recti.
- Alcohol addiction determinate speed up blood flow in anal area, that consequently provoke hemorrhoidal bleeding.
- Excessive physical activity and lifting of heavy things is the reason of increase of pressure in abdominal cavity that consequently can be reason of hemorrhoids.
- Spicy food provoke irritation in anal area.
Clinical sign of hemorrhoidal disease
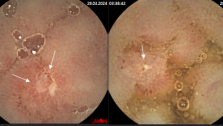
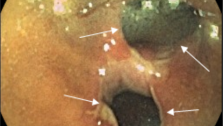
Traditionally hemorrhoids are characterized by two most principal symptoms- bleeding (51%) and prolapse of cavernous bodies out of anal canal (37%). For hemorrhoids are also common following symptoms: anal scratch (9%), anal discomfort (5%), and mucus hypersecretion (2%).
Hemorrhoids can be acute and chronic, but properly both of them are stages of the one process. Chronic hemorrhoid is characterized by arterial blood segregation triggered by defecation, hemoroidal prolapse, chronic aching anal pain, scratch.
Acute hemorrhoids (hemorrhoidal thrombosis) is characterized by acute decrease of venous blood drainage (thrombosis). Clinical signs of acute hemorrhoids are: anal pain, prolapse and swelling of cavernous body which doesn’t reset in anal canal, its inflammation. The patients with this diagnosis need urgent medical care. Mucous wall inflames and ulcerates because of dilatation of venous plexus.
There are three degrees of acute hemorrhoid:
- First degree is characterized by the hemorrhoidal thrombosis without inflammation of piles. Palpation of piles is painful. Perianal skin is slightly redness. The character complaints are sense of burning and itch, which increase during bowel movement.
- Second degree is characterized by addition of inflammation. There are more manifest edema and redness of perianal area. Palpation and digital examination are very painful. Patients usually complain about strong pains in anal canal, which increases in sitting position and when they are walking.
- Third degree is characterized by inflammation of the tissue around hemorrhoids, all anus is swelling. Palpation of piles is very painful. Thrombosed internal purple hemorrhoids covered by fibrin are prolapsed from anal canal. If treatment was not carried out on time can appear necrosis of hemorrhoids. Mucous membrane, which covering cavernous bodies, ulcerate, becomes black with fibrin stratifications. In some neglected cases, hemorrhoidal thrombosis can be complicated by anal abscess (difficult complication).
The most common signs of chronic hemorrhoids are discomfort, itch in an anal channel (they are related to the irritation of inferior part of anal canal and perianal skin by intestinal mucus), bleeding during and after bowel movement, prolapse of internal piles.
Classification of hemorrhoids based on level of their dilatation and prolapse
- No prolapse.
- The prolapse spontaneously re-enters the anal canal when straining stops.
- The prolapse does not spontaneously return into the anal canal, and has to be pushed back in.
- Permanente prolaps, recurring after attempts to push it back in.
Diagnostic of hemorrhoids
Diagnostic of hemorrhoids is not difficult. Usually diagnosis of hemorrhoidal disease requires only inspection and physical examination.
During physical examination there is important to evaluate the level of hemorrhoidal prolapse, the possibility to return them into the anal canal, skin around anal canal, signs of bleeding. The next examination is rectosigmoidoscopy (that makes it possible to examine mucous membrane of rectum and sigmoid bowel to exclude oncology diseases).
Differential diagnosis of hemorrhoids:
- Anal fissure (also can be bleeding and pain in anal canal);
- Rectal prolapse (circular prolaps in anal area);
- Rectal cancer (bleeding also occurs).
The treatment of hemorrhoids
The treatment of acute hemorrhoids depends on stage of disease. Only patients with third degree of acute hemorrhoid should be operated (we perform hemorrhoidectomy).
For first and second degrees of acute hemorrhoids, we indicate medical treatment.
1. To eliminate pain conditional by thrombosis and acute anal fissure we use analgesics by systemic route and local medications, which consist a combination of anti-inflammatories and analgesics (Posterisan, Posterisan forte).
2. There is necessary to prescribe phlebotonic drugs.
3. In case of bleeding, we use suppositories with adrenalin and local haemostatic treatment. Conservative treatment of hemorrhoids supplies temporal effect, and risk of recurrence is quite high. That is why when escalation is healed we recommend one of microinvasive techniques or operation that depends on the stage of hemorrhoid. For chronic hemorrhoids (first and second stages), conservative treatment mostly is effective, but often this treatment is required for them during all there life. High-fiber diet, refusal of alcohol and spicy food, regulation of bowel movement, prophylaxis of trauma of this area, washing after defecation, suppositories and ointments help patients with hemorrhoid practically avoid discomfort.
Conservative treatment of chronic hemorrhoids includes phlebotonic drugs, suppositories with anti-inflammatory and analgesic, microenema with medications. There is necessary to admit that any treatment of hemorrhoid can be not high effective if other gastrointestinal diseases, first of all, of large bowel, that patient have, are not treated. There is important to treat concomitant colitis and eliminate constipation (Forlax).
- If patient has first- or second- degree- hemorrhoids, but escalation and bleeding occurs often there is possible to perform microinvasive techniques.
- For treatment of first-degree- hemorrhoids in our department we use infrared coagulation.
- For treatment of second-degree- hemorrhoids, we apply infrared coagulation, Rubber band ligation of hemorrhoidal piles, Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialisation (THD).
- For treatment of third-degree- hemorrhoids, we apply rubber bang ligation, Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialisation (THD).
- For treatment of fourth -degree- hemorrhoids, we apply Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialisation (THD), Longo operation and operations (Milligan-Morgan, Parks, Waithead methods).